

Hardened Steel 20MnCr5 Gears
20MnCr5 is a low-alloy case-hardening steel widely used for automotive and industrial gears. Its chemical composition (approx. 0.17–0.22% C, 1.1–1.4% Mn, 0.9–1.2% Cr) makes it suitable for carburizing, quenching, and tempering.
Hard turning with cubic boron nitride (CBN) inserts has become a mainstream alternative to grinding for finishing hardened steels in many gear-manufacturing applications. For gears made from case-hardened low-alloy steels such as 20MnCr5 (EN designation), CBN turning offers short cycle times, simplified process flow, and competitive surface integrity when applied correctly.
Why 20MnCr5 for Gears?
-Wear resistance: hard case resists pitting, scuffing, and abrasive wear.
-Fatigue strength: compressive residual stresses in the case improve bending and contact fatigue life.
1)-Tough core: prevents brittle fracture under impact loads.
-Machinability: relatively good in the annealed state before hardening.
Applications of 20MnCr5:
* Automotive transmission gears and shafts.
* Industrial gearboxes and powertrain components.
* Bearings, cams, and other high-load wear components.
Machining Hardened 20MnCr5 Gears
1) Before hardening, gears are typically cut by hobbing, shaping, or broaching in the soft state.
2) After hardening: finishing operations include grinding, honing, or hard turning (with CBN inserts) to meet tight tolerances and surface finish requirements.
3) Superfinishing: in high-performance applications (e.g., automotive transmissions), superfinishing or polishing films are used to reduce Ra <0.2 µm and improve efficiency.
Choosing the right cutting tools for machining hardened 20MnCr5 gears is crucial because this material combines very high surface hardness (58–62 HRC in the carburized layer) with a tougher core. Tooling choice determines not only tool life but also surface finish, profile accuracy, and overall cost per part.
Material Challenges
* Case-hardened layer (58–62 HRC): very abrasive, requires superhard cutting tools.
* Variable hardness (case vs. core): tool must handle transitions in hardness.
* Interrupted cuts: gears often involve cutting across teeth roots and flanks, which stresses the cutting edge.
* Surface finish demands: Ra ≤ 0.4 µm in most gear applications, sometimes lower.
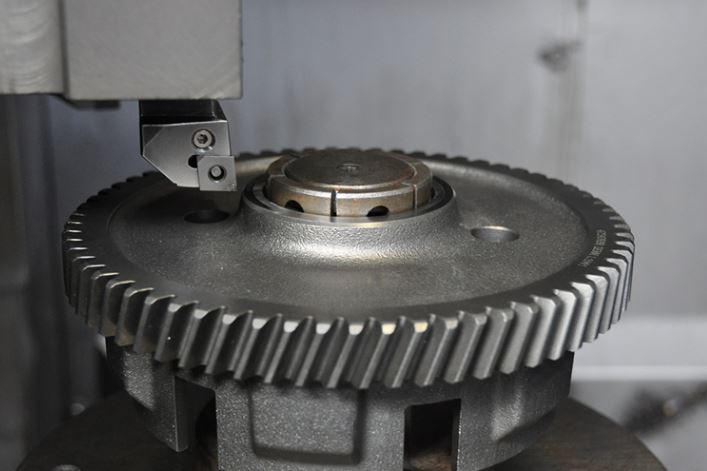

Tool Material Selection
* CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) inserts
-Best choice for hard turning after heat treatment.
-Excellent wear resistance, hot hardness, and ability to cut dry.
-Recommended for finishing the gear tooth flanks and precision surfaces.
Ceramic (Al2O3 + TiCN whisker-reinforced) insert
-Alternative to CBN for continuous cutting at very high speeds.
-Less tough — not ideal for interrupted cuts on gears.
PCD (Polycrystalline Diamond) inserts
-Not suitable — reacts with iron at high temps (rapid wear).
Carbide (coated/uncoated) insert
-Limited to pre-hard turning (<45 HRC) or rough machining before heat treatment.
Recommendation: Use CBN inserts for finishing hardened 20MnCr5 gears. Use carbide tools only in the soft state before hardening.
Advantges of CBN insert for machining hardened steel 20MNCR5 gears
1. Ability to Machine Very Hard Materials
-CBN retains hot hardness up to ~1400°C and is second only to diamond in hardness.
-It easily cuts the 58–62 HRC case-hardened layer of 20MnCr5 gears, where carbide tools would fail quickly.
2. Excellent Tool Life and Consistency
-High resistance to abrasive wear from the hardened martensitic case.
-Predictable wear patterns (mainly flank wear), which makes tool life stable and repeatable in production.
-Fewer tool changes → less downtime.
3. Superior Surface Finish
-CBN inserts with proper geometry can achieve Ra 0.2–0.4 µm, meeting or replacing many grinding operations.
-Wiper-style CBN inserts can maintain good finish at higher feeds, increasing productivity without sacrificing quality.
4. Process Efficiency (Hard Turning vs. Grinding)
-Hard turning with CBN can replace finish grinding in many gear applications.
-Eliminates the need for multiple machines and setups (e.g., turning + grinding).
-Shorter cycle times → lower cost per part.
5. Surface Integrity Benefits
Hard turning with CBN often induces beneficial compressive residual stresses on the gear flank surface, improving fatigue strength.
Produces a white layer–free surface (if parameters are controlled), unlike aggressive grinding that can cause burn or tensile stresses.
6. Dry Cutting Capability
CBN is highly thermally stable, so machining can be performed dry or with MQL.
Eliminates coolant costs and avoids thermal cracking issues caused by intermittent coolant flow.
Environmentally friendlier process compared to flood grinding.
7. Flexibility in Gear Finishing
-Profile accuracy: CBN inserts can be custom-shaped to finish gear tooth profiles in one pass.
-Suitable for both continuous and interrupted cuts (when using tougher CBN grades).
-Can be applied to small batch or high-volume production with equal efficiency.
8. Lower Overall Manufacturing Cost
-Although CBN inserts are more expensive per unit, they reduce total cost per part by:
-Longer life → fewer inserts used.
-Faster cycle times.
-Eliminating or minimizing secondary grinding operations.
-Reducing setup and handling time.
Recently Moresuperhard receive one inquirey about CBN insert for machining hardened steel 20MNCR5 gears, lets see it together:
Workpiece | Gear |
Hardness | 60 HRC |
Currently brand used | MITSUBISHI |
Inserts model | |
Outer diameter | 180mm |
Maching | CNC turning, rough machining, heavy interrupted machining, dry machining |
Processing parameters | S-283 RPM VC-160 Fn - 0.12 Ap - 0.5 mm |
Workpiece material | 20MNCR5 |
---EDITOR: Doris Hu,Erin Zhang
---POST: Doris Hu
Semiconductor Industry Solutions
PCD & PCBN Tools Grinding Industry
Diamond Cutting Bruting Polishing
Add: No.171 Zhongyuan Rd, Zhongyuan District, Zhengzhou, 450001, Henan, China
Tel: +86-371-86545906
Phone / Whats App: +86 18339903057
E-mail: [email protected]



